Your browser doesn't support the features required by impress.js, so you are presented with a simplified version of this presentation.
For the best experience please use the latest Chrome, Safari or Firefox browser.
# 编译链接和运行时库
-----
# 编译
C语言编译步骤:
1. 预处理 `gcc -E hello_world.c`
2. 编译 `gcc -S hello_world.c`
3. 汇编 `gcc -c hello_world.c`
4. 链接 `gcc hello_world.c`
-----
# 编译步骤
1. 词法分析(flex)
2. 语法分析(bison)
3. 语义分析
4. 中间代码生成
5. 目标代码生成优化(llvm IR)
-----
# 代码演示1:
1. scanner.l
2. parser.y
3. 遍历语法树
-----
## 链接
2. 为什么需要链接 ?
2. ELF文件的结构是什么样子的 ?
3. section 和 segment 的区别是什么 ?
4. 静态链接的过程是什么样子的 ?
5. 强符号和弱符号
3. 为什么需要动态链接 ?
4. 如何降低动态链接的性能损失
-----
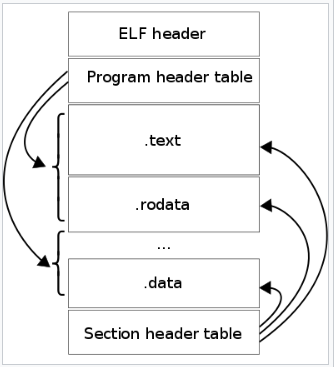
## ELF文件的结构
1. ELF Header
2. Program Header
3. Section Header
-----
# Hack ELF Header
typedef struct
{
unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT]; /* Magic number and other info */
Elf64_Half e_type; /* Object file type */
Elf64_Half e_machine; /* Architecture */
Elf64_Word e_version; /* Object file version */
Elf64_Addr e_entry; /* Entry point virtual address */
Elf64_Off e_phoff; /* Program header table file offset */
Elf64_Off e_shoff; /* Section header table file offset */
Elf64_Word e_flags; /* Processor-specific flags */
Elf64_Half e_ehsize; /* ELF header size in bytes */
Elf64_Half e_phentsize; /* Program header table entry size */
Elf64_Half e_phnum; /* Program header table entry count */
Elf64_Half e_shentsize; /* Section header table entry size */
Elf64_Half e_shnum; /* Section header table entry count */
Elf64_Half e_shstrndx; /* Section header string table index */
} Elf64_Ehdr;
-----
# 演示代码2
-----
# Hack Program Header
typedef struct
{
Elf64_Word p_type; /* Segment type */
Elf64_Word p_flags; /* Segment flags */
Elf64_Off p_offset; /* Segment file offset */
Elf64_Addr p_vaddr; /* Segment virtual address */
Elf64_Addr p_paddr; /* Segment physical address */
Elf64_Xword p_filesz; /* Segment size in file */
Elf64_Xword p_memsz; /* Segment size in memory */
Elf64_Xword p_align; /* Segment alignment */
} Elf64_Phdr;
-----
# 演示代码3 :
首先看一段代码
#include
extern char end;
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
printf("%p\n", &end);
return 0;
}
-----
# Section Header
typedef struct
{
Elf64_Word sh_name; /* Section name (string tbl index) */
Elf64_Word sh_type; /* Section type */
Elf64_Xword sh_flags; /* Section flags */
Elf64_Addr sh_addr; /* Section virtual addr at execution */
Elf64_Off sh_offset; /* Section file offset */
Elf64_Xword sh_size; /* Section size in bytes */
Elf64_Word sh_link; /* Link to another section */
Elf64_Word sh_info; /* Additional section information */
Elf64_Xword sh_addralign; /* Section alignment */
Elf64_Xword sh_entsize; /* Entry size if section holds table */
} Elf64_Shdr;
-----
# 说明几个关键的Section
1. .text
2. .data
3. .rodata
4. .bss
5. .got
-----
# 静态链接: 链接前
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 :
0: 55 push %rbp
1: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
4: 48 83 ec 10 sub $0x10,%rsp
8: 89 7d fc mov %edi,-0x4(%rbp)
b: 48 89 75 f0 mov %rsi,-0x10(%rbp)
f: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
14: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 19 (main+0x19)
19: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
1e: c9 leaveq
1f: c3 retq
-----
# 静态链接: 链接后
0000000000001119 :
1119: 55 push %rbp
111a: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
111d: 48 83 ec 10 sub $0x10,%rsp
1121: 89 7d fc mov %edi,-0x4(%rbp)
1124: 48 89 75 f0 mov %rsi,-0x10(%rbp)
1128: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
112d: e8 07 00 00 00 callq 1139
1132: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
1137: c9 leaveq
1138: c3 retq
0000000000001139 :
1139: 55 push %rbp
113a: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
113d: 90 nop
113e: 5d pop %rbp
113f: c3 retq
-----
# 和静态链接相关的Section 和结构体
1. .symtab
2. .rel.text .rel.data
typedef struct {
Elf64_Word st_name; /* Symbol name (string tbl index) */
unsigned char st_info; /* Symbol type and binding */
unsigned char st_other; /* Symbol visibility */
Elf64_Section st_shndx; /* Section index */
Elf64_Addr st_value; /* Symbol value */
Elf64_Xword st_size; /* Symbol size */
} Elf64_Sym;
typedef struct { // 重定位入口
Elf64_Addr r_offset; /* Address */
Elf64_Xword r_info; /* Relocation type and symbol index */
/* 低8位表示类型,高24表示在符号表中间的下标 */
} Elf64_Rel;
-----
# 静态链接的两种方法
1. PC相对寻址
2. 绝对寻址
符号的实际地址 + 保存在被修正位置的值 (- 被修正的位置)
-----
# 动态链接
1. GOT(Global Offset Table)
2. PLT(Procedure Linkage Table)
-----
# 延迟绑定的实现
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
printf("%d\n", 1);
return 0;
}
-----
# 延迟绑定的实现
0000000000001139 :
1139: 55 push %rbp
113a: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
113d: 48 83 ec 10 sub $0x10,%rsp
1141: 89 7d fc mov %edi,-0x4(%rbp)
1144: 48 89 75 f0 mov %rsi,-0x10(%rbp)
1148: be 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%esi
114d: 48 8d 3d b0 0e 00 00 lea 0xeb0(%rip),%rdi # 2004 <_IO_stdin_used+0x4>
1154: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
1159: e8 d2 fe ff ff callq 1030 (printf@plt)
115e: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
1163: c9 leaveq
1164: c3 retq
1165: 66 2e 0f 1f 84 00 00 nopw %cs:0x0(%rax,%rax,1)
116c: 00 00 00
116f: 90 nop
-----
# 延迟绑定的实现
printf@plt:
jmp * (printf@GOT)
push n
push ModuleID
jump _dl_runtime_resolve
-----
# 延迟绑定的实现
printf@plt:
jmp * (printf@GOT)
push n
push ModuleID
jump _dl_runtime_resolve
Disassembly of section .plt:
0000000000001020 (.plt):
1020: ff 35 e2 2f 00 00 pushq 0x2fe2(%rip) # 4008 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+0x8)
1026: ff 25 e4 2f 00 00 jmpq *0x2fe4(%rip) # 4010 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+0x10)
102c: 0f 1f 40 00 nopl 0x0(%rax)
0000000000001030 (printf@plt):
1030: ff 25 e2 2f 00 00 jmpq *0x2fe2(%rip) # 4018 (printf@GLIBC_2.2.5)
1036: 68 00 00 00 00 pushq $0x0
103b: e9 e0 ff ff ff jmpq 1020 (.plt)
-----
## 链接
2. 为什么需要链接 ?
2. ELF文件的结构是什么样子的 ?
3. section 和 segment 的区别是什么 ?
4. 静态链接的过程是什么样子的 ?
5. 强符号和弱符号
3. 为什么需要动态链接 ?
4. 如何降低动态链接的性能损失
-----
# 运行时库
-----
## 一些问题
1. main函数是程序执行的第一行吗?
2. malloc是如何实现的 ?
4. 如何不使用glibc实现io
4. 变长数组如何实现 ?
-----
# 运行时库
1. 启动和退出函数
2. 辅助工具函数(string math)
3. IO
3. **HEAP**
4. 调试功能
-----
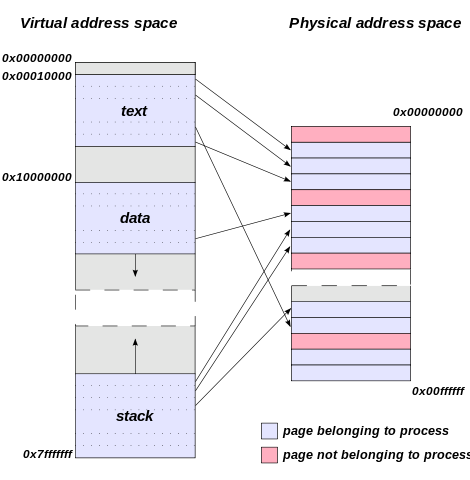
# 进程地址空间
-----
# 代码4: 自定义C语言运行时库
-----
# 说明几点
1. 汇编代码和64位机器的兼容
2. 变长参数
3. 修复Heap 实现的Bug
4. 调用惯例
5. 错误的链接脚本
-----
## 一些问题
1. main函数是程序执行的第一行吗?
2. malloc是如何实现的 ?
4. 如何不使用glibc实现io
4. 变长数组如何实现 ?
-----
# 疑惑
当使用write系统调用的时候,为什么不可以将用户栈地址作为参数 ?